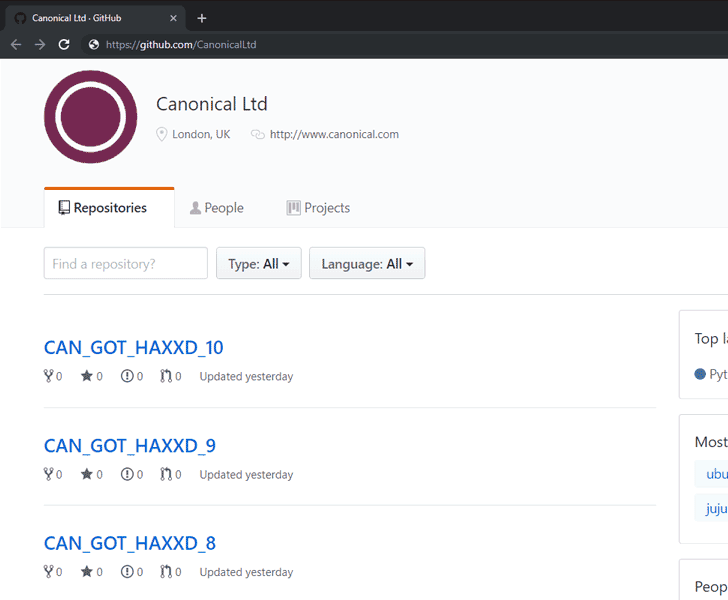
Ubuntu-Maker Canonical's GitHub Account Gets Hacked
An unknown hacker yesterday successfully managed to hack into the official GitHub account of Canonical, the company behind the Ubuntu Linux project and created 11 new empty repositories.
It appears that the cyberattack was, fortunately, just a "loud" defacement attempt rather than a "silent" sophisticated supply-chain attack that could have been abused to distribute modified malicious versions of the open-source Canonical software.
In a statement, David from Canonical confirmed that attacker(s) used a Canonical owned GitHub account whose credentials were compromised to unauthorizedly access Canonical's Github account.
"We can confirm that on 2019-07-06 there was a Canonical owned account on GitHub whose credentials were compromised and used to create repositories and issues among other activities," David said.
"Canonical has removed the compromised account from the Canonical organization in GitHub and is still investigating the extent of the breach, but there is no indication at this point that any source code or PII was affected."
David also confirmed that since the company now uses Launchpad hosting platform to build and maintain Ubuntu distributions, unauthorized changes on its Github account doesn't affect its popular and widely-used Linux operating system and its million of users.
"Furthermore, the Launchpad infrastructure where the Ubuntu distribution is built and maintained is disconnected from GitHub, and there is also no indication that it has been affected," David added.
"We plan to post a public update after our investigation, audit, and remediations are finished. Thank you, your trust in Canonical is important to us, which is why we take privacy and security a priority."
The company is currently reviewing the source code available on GitHub to investigate the extent of the breach and have promised to share more details about the incident shortly.
Last year, GitHub account of Gentoo Linux distribution was also hacked using password-guessing attack, and attackers successfully managed to replace the content of its repositories and pages with malware.
Stay tuned for more information on this incident.
It appears that the cyberattack was, fortunately, just a "loud" defacement attempt rather than a "silent" sophisticated supply-chain attack that could have been abused to distribute modified malicious versions of the open-source Canonical software.
In a statement, David from Canonical confirmed that attacker(s) used a Canonical owned GitHub account whose credentials were compromised to unauthorizedly access Canonical's Github account.
"We can confirm that on 2019-07-06 there was a Canonical owned account on GitHub whose credentials were compromised and used to create repositories and issues among other activities," David said.
"Canonical has removed the compromised account from the Canonical organization in GitHub and is still investigating the extent of the breach, but there is no indication at this point that any source code or PII was affected."
David also confirmed that since the company now uses Launchpad hosting platform to build and maintain Ubuntu distributions, unauthorized changes on its Github account doesn't affect its popular and widely-used Linux operating system and its million of users.
"Furthermore, the Launchpad infrastructure where the Ubuntu distribution is built and maintained is disconnected from GitHub, and there is also no indication that it has been affected," David added.
"We plan to post a public update after our investigation, audit, and remediations are finished. Thank you, your trust in Canonical is important to us, which is why we take privacy and security a priority."
The company is currently reviewing the source code available on GitHub to investigate the extent of the breach and have promised to share more details about the incident shortly.
Last year, GitHub account of Gentoo Linux distribution was also hacked using password-guessing attack, and attackers successfully managed to replace the content of its repositories and pages with malware.
Stay tuned for more information on this incident.
Have something to say about this article? Comment below or share it with us on Facebook, Twitter or our LinkedIn Group.